Cloud-Based ADS Supports Participation in Ancillary Services Market
Oct 06, 2023
Folsom, CA, October 6, 2023 – Trimark has introduced cloud-based, Automatic Dispatch System (ADS) services to help small BESS and…
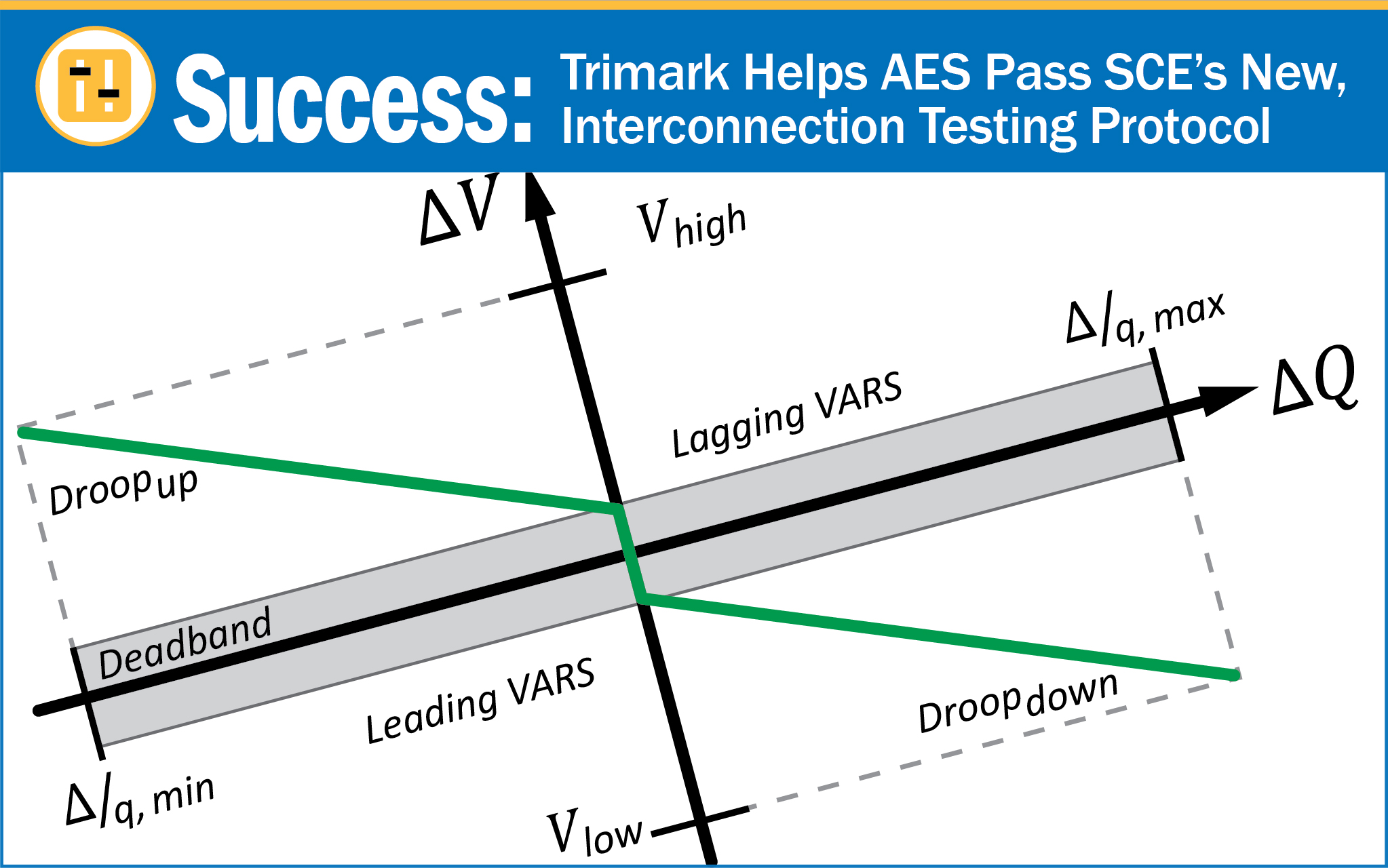
Trimark Associates, Inc. (Trimark) successfully completed pilot testing for the first resources to pass Southern California Edison’s (SCE) strict, new, Interconnection Performance Requirements. AES’ Raceway and Estrella Photovoltaic (PV) plus Battery Energy Storage (BESS) projects are the first two resources to pass SCE’s new testing protocol which is now required to reach commercial operation.
Based on IEEE 2800, SCE’s new Interconnection Performance Test applies a witnessed approach to validate that the PV and BESS resources respond in accordance with SCE’s performance standards. Trimark collaborated with AES and SCE to apply the testing procedures in a safe and efficient manner.
Raceway and Estrella are co-located PV+BESS resources connected to SCE’s Polaris substation which feeds into the Big Sky Substation, near Lancaster, California. Raceway includes 125 MW PV plus 80 MW (320 MWh) BESS. Estrella includes 56 MW PV plus 28 MW (112 MWh) BESS. Each resource includes a Trimark Power Plant Controller (PPC) that communicates and coordinates its actions in parallel with 22 PV and BESS resources that provide over 1 GW of power to Big Sky. All resources in this enterprise are controlled and monitored with Trimark’s SCADA platform.
Big Sky is important for another reason as well – it’s the aggregation point for delivering more than 1 GW of renewable power to SCE’s electric grid. At SCE’s interconnection substation, a network of revenue meters track energy from each resource for use in settling transactions. The meter data also informs the control algorithms used in the advanced power plant controls.
Most new renewable power resources use PV, BESS, or a combination of the two. To address this trend, IEEE issued their 2800 standard which expands on the IEEE 1547 standard for Interconnection and Interoperability. Specifically, IEEE 2800 addresses challenges, and opportunities, afforded by inverter-based resources. SCE refined 2800 to define practical targets for a variety of power management performance requirements including reaction time, ramp rate, rise time, droop, voltage step testing, overshoot, deadband, settling time, and settling band. These targets are primarily applicable to controlling Primary Frequency Response (PFR) and voltage.
Previously, these standards served as guidelines. Resource owners could simply submit data from simulations of voltage and frequency events. However, SCE has now tightened its approach to ensure testing integrity, one way of validating that every new resource aligns with their grid performance model.
“SCE requires the resource to complete successful, real-time voltage system step testing,” explained Stephen Yee, Trimark’s Director of SCADA controls. “In this test, an SCE transmission system operator (TSO) can generate a true grid voltage event by engaging grid capacitor or reactor banks.”
“One test requires initiating a system voltage step change at the substation, then measuring how quickly the control system responds and reacts,” said Yee. “The control system polls meter voltage values at the point of interconnection, then adjusts reactive power at the site to meet the required target at the point of measurement. The response time must consider network latency, PID processing time, meter response time, inverter reaction time, and time to stabilize the new value. In fact, every resource that feeds the Polaris substation uses Trimark controls, so every site detected the change and responded automatically – all within the required reaction time.”
“One of SCE’s tests requires that the system react within 500 milliseconds (ms) of detecting the grid event – that’s particularly important where primary frequency response is concerned,” said Yee. “For the PFR performance test, Trimark’s control system corrected the active power with 50% of the required active power PFR offset in response to a 1 Hertz change within 352 ms. In all cases, Trimark’s control system exceeded the minimum requirements set by SCE.”
The 22 resources that feed the Big Sky substation are spread across many miles of the Western Mojave desert. That environment results in varying power loss depending on the distance between the sites and the substation. Power values also vary depending on resource size, dispatch target, generating conditions, line characteristics, transformer losses, and more. Finally, the operating status of every resource on a generation tie line affects every other associated resource. These dynamically changing power values not only impact settlements, they are a critical consideration in the control logic as well.
To address these challenges, Trimark built a sophisticated dynamic loss compensation system – a network of revenue meters that exchange real time data to support accurate metering values. The Raceway and Estrella projects alone require 16 meters. The entire Big Sky enterprise uses almost 100 revenue-grade meters.
“Meter values tell the control system exactly what’s happening at the point of delivery regarding real power, reactive power, voltage, and frequency,” said Yee. “This realtime feedback loop provides data our systems need to automatically meet precise setpoints and synchronize with the electric grid.”
Trimark worked with AES (owner) and Dashiell (EPC) to bring Raceway and Estrella to commercial operation. Trimark also provided control systems, metering, Remote Intelligent Gateways, and network devices at 20 other resources in the Big Sky enterprise. Across the US, Trimark has helped AES develop, support and effectively operate more than 550 renewable power resources.
Trimark’s solution includes SCADA, site networking devices, revenue metering, and a Remote Intelligent Gateway (RIG).
Trimark Associates, Inc. delivers industry-leading solutions that provide real-time operational control, enable informed management of power production operations, ensure regulatory compliance, and maximize revenue. Trimark’s turnkey products, engineering, and customer support services control, measure, and manage all aspects of power production that utility-scale power producers require to maintain peak business performance and achieve financial goals.

Trimark will exhibit at Intersolar North America / Energy Storage North America (ESNA) January 17 to 19, 2024 in the…
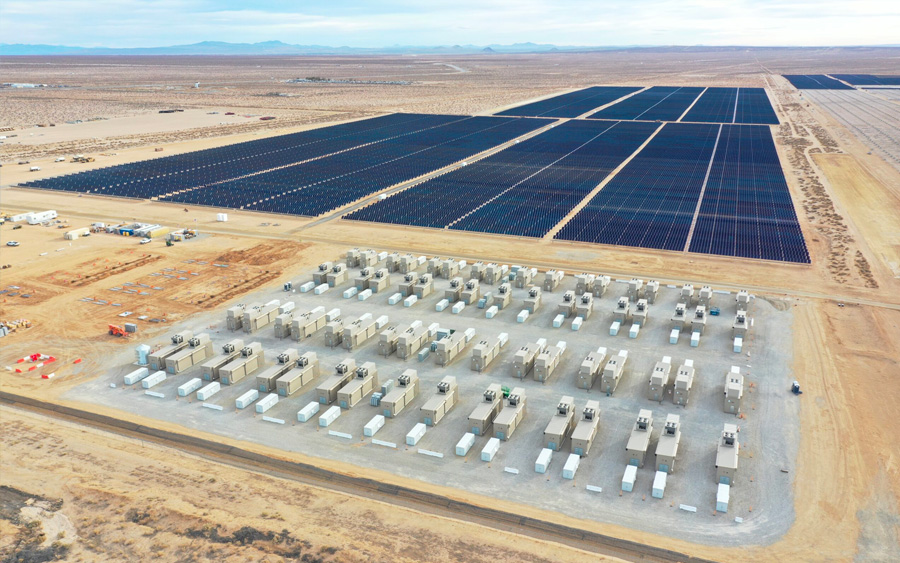

The Edwards & Sanborn project redefines the utility-scale PV+Storage landscape. Folsom, CA, February 17, 2021 – Trimark Associates, Inc. is…

Controller to Lead Trimark Accounting Team and Processes Folsom, CA, April 28, 2023 – Trimark Associates, Inc. (Trimark), the industry…

Project Type: 2 Co-located PV sites rated at 20 MW (Summer) & 1.5 MW (Winter) Location: San Joaquin, CA EPC:…
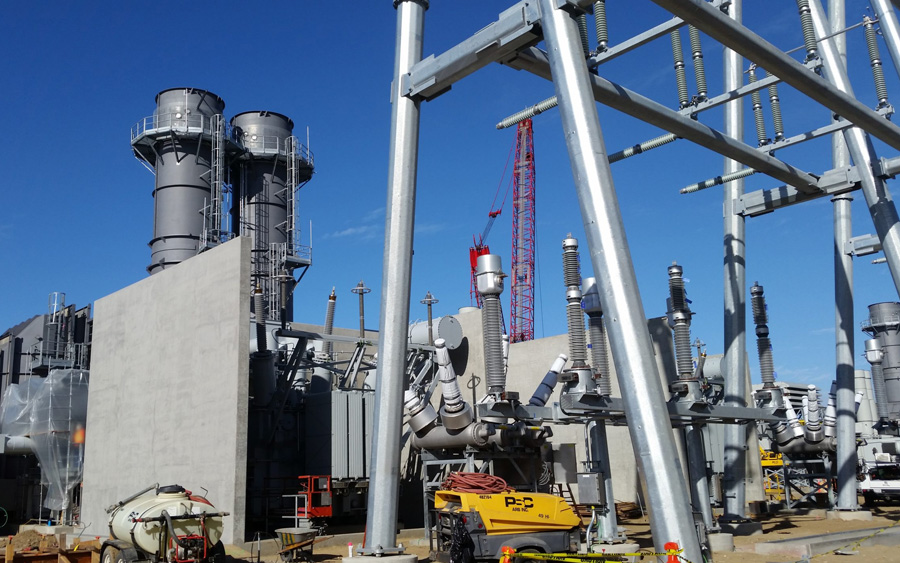

Project Type: 527 MW natural gas-fueled electricity generating plant Location: Carlsbad, CA Client/EPC: NRG Energy Products/Services: Trimark integrated ADS into…
Need a SCADA system that optimizes revenue?
Need help meeting interconnection requirements?
Want to stay in the market and avoid fines?
Weʼve got you!
Get Started Today